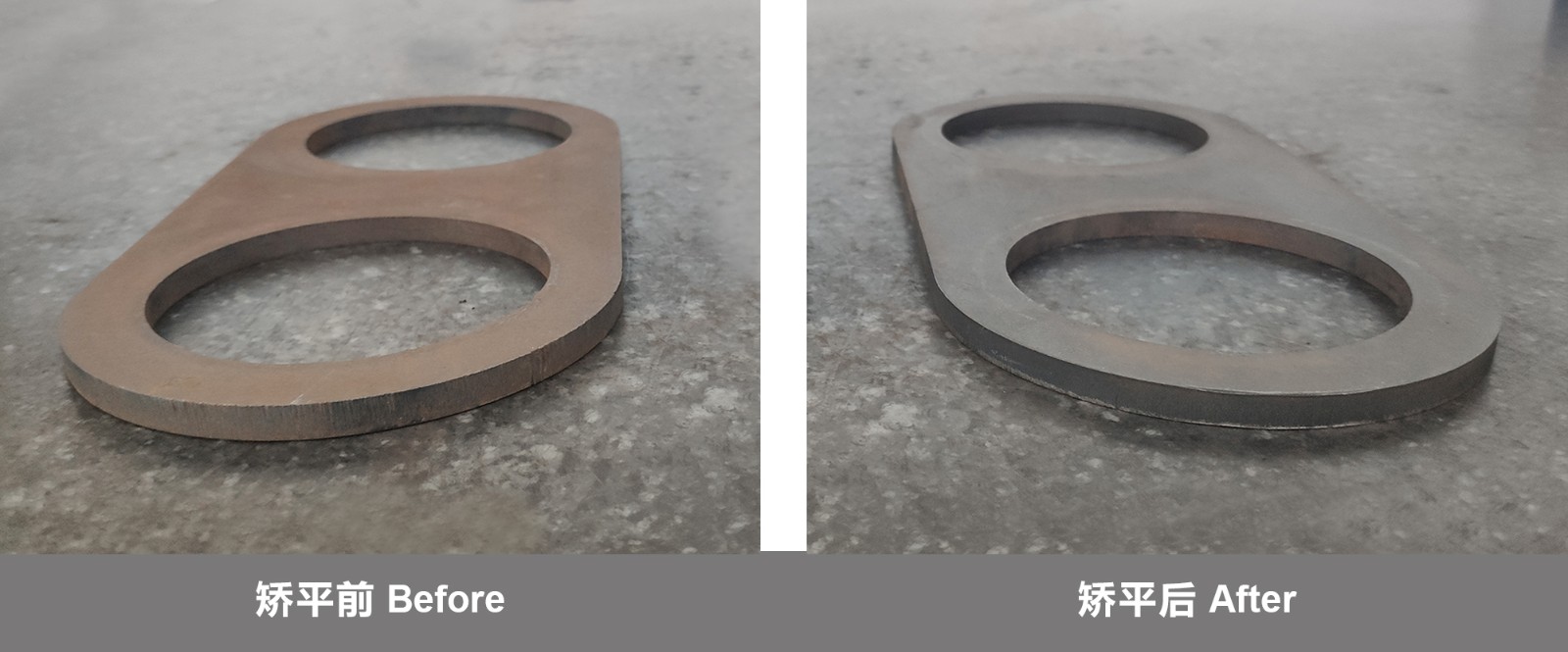
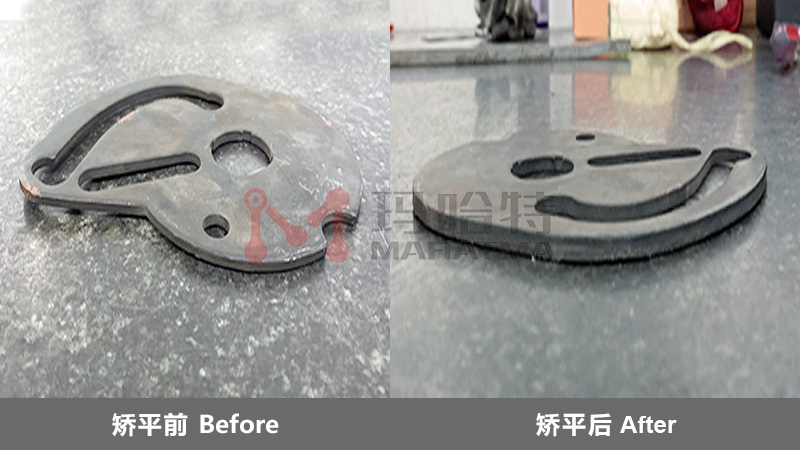
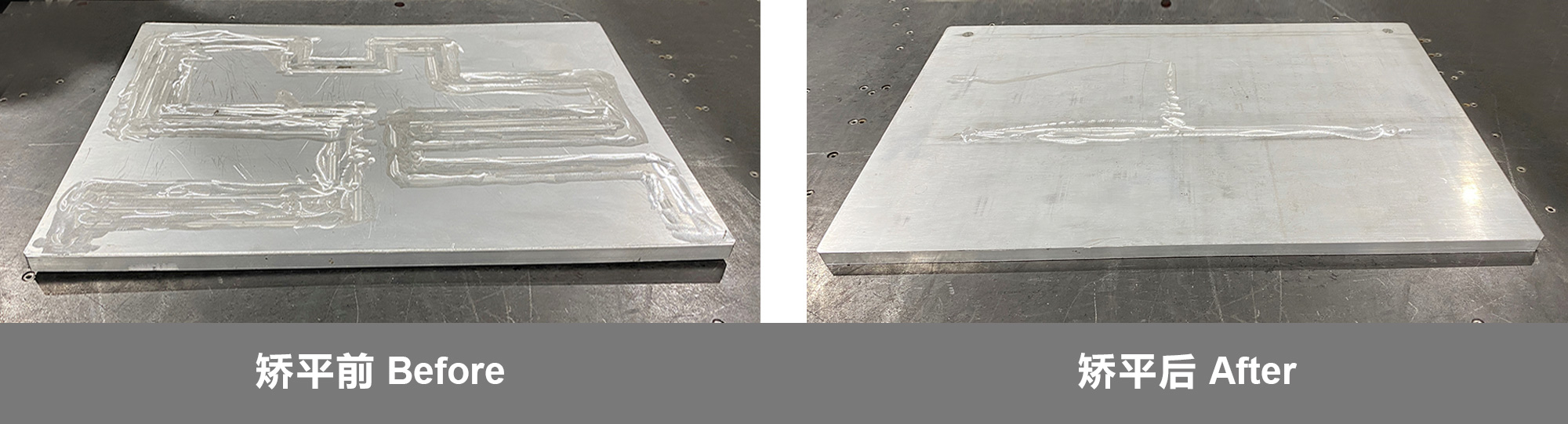
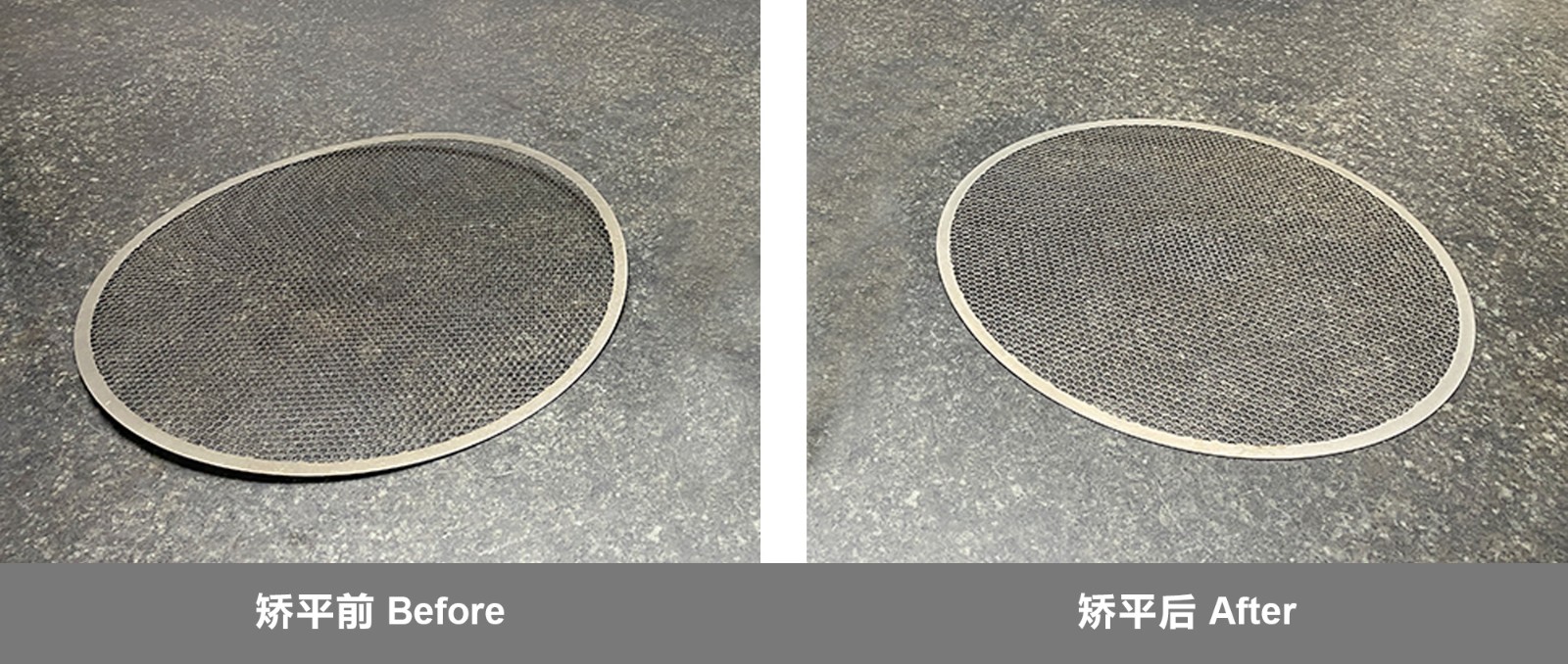
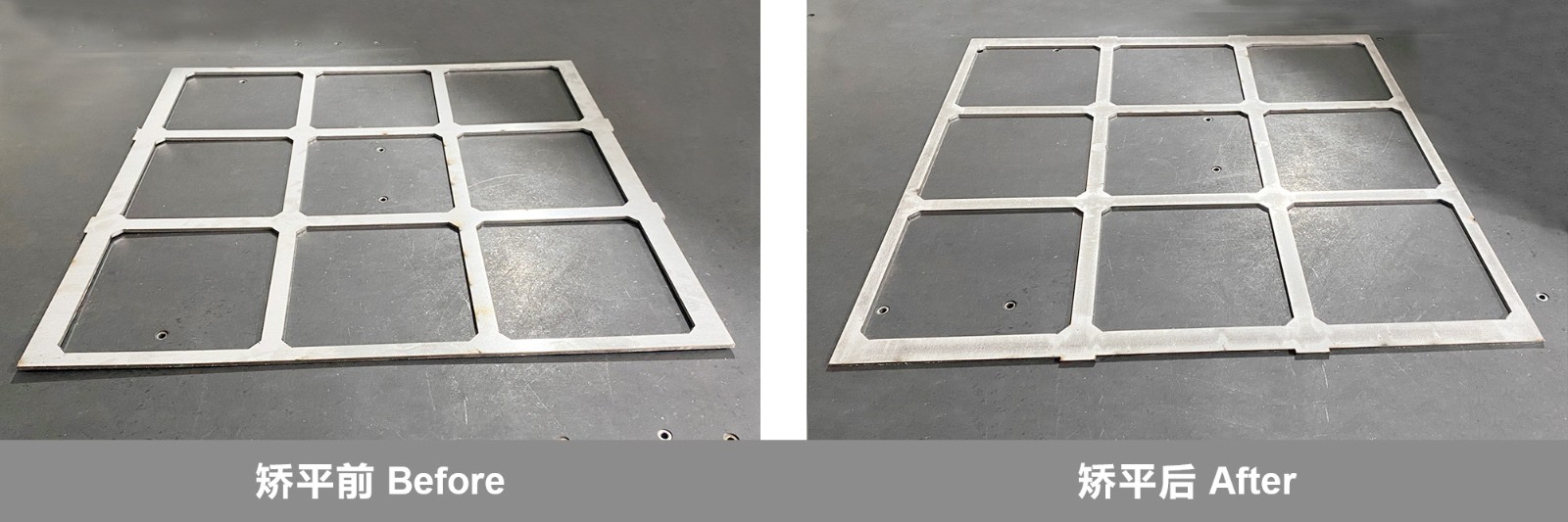
For sheet metal leveling, MAHATMA strives to provide precise and innovative sheet metal processing for every customer. From extremely thin and small sheet metal parts to thick plates, our high-efficiency leveling machine can solve various unevenness problems, so that the workpiece can be leveled with almost no internal stress, and greatly reduce the trouble of waste and rework.

Sheet metal - the most important type and the most common form
As rolled metal products, sheet metal has many different forms. It is very important to distinguish coil and sheet. Coil material is a kind of wound metal belt, which weighs several tons and is usually hundreds of meters long. Sheet metal (also known as sheet metal) is a rectangular thin plate with a certain length cut from the coil. The steel coils of the steel plant will be processed into smaller coils or plates (or plates), and then they will be delivered to the sheet metal processor according to the correct size and quantity. In addition to steel and stainless steel, almost all metals, from precious metals, such as gold and silver, to various steel alloys and aluminum, can be made into sheet metal. The length and width of the sheet metal are always greater than the thickness value.
Sheet metal is generally divided into thin plate and thick plate. Thin plate refers to the plate with thickness less than 3mm, which is usually cut from the coil. On the contrary, the thickness of thick plates exceeds 3mm.

Laser cutting, cutting or stamping - the most common sheet metal processing technology
1. there are many methods for cutting sheet metal, and the most commonly used processes are:
Stamping:
During stamping, metal stamping parts are formed from sheet metal by manual, automatic press, punch, or stamping tools. Stamping is mainly applied to the production of small parts directly processed from the flat coil belt.
Undercut (electric shear):
The characteristics of undercut technology are reflected in its split seam, cutting process independent of cutting tools and free cutting shape.
A punching shear with an opening on one side cuts sheet metal parts through a cutting tool that engages up and down repeatedly. This tool can be manually or electrically controlled, but can only be used by hand. In addition, undercut is a very rough process, and its application is gradually decreasing.
Laser cutting:
This method is to cut the metal plate by the heat of the laser beam. Laser is a highly flexible tool, especially suitable for the processing of thin plates. Laser cutting is the most commonly used method in flexible metal plate processing. It requires the most fine cut and the highest quality.
Plasma cutting:
This is a thermal cutting method, which uses the heat of the plasma flow to liquefy the material. The high kinetic energy of the plasma stream blows the liquefied material out of the notch. Plasma cutting is mainly used for metal plates with thickness between 50 mm and 10 mm.
Flame cutting (oxygen cutting):
During this cutting process, the plates are heated to ignition temperature using oxygen and gas (e.g. acetylene, MAPP, propylene, propane or natural gas). Adding oxygen creates a cut that separates the sheet metal. Flame cutting is the most commonly used method for cutting extremely thick materials.




